Cybersecurity Risk Management

Availability on Premium & Ultimate subscription plan.
The Cybersecurity Risk Management module provides organizations with a structured and effective way to identify, assess, and mitigate information security risks. It is built on ISO/IEC 27001 and is aligned with ISO/IEC 27005:2022, and serves as a risk register that helps businesses evaluate and manage risks in a systematic manner.
Also, it uses ISO/IEC 27554:2024, which applies ISO 31000 risk management principles to identity-related risks. This helps organizations assess threats related to identity management and security.
This module helps organizations identify risks and create plans to reduce them. It can be used alone or as part of a larger security plan.
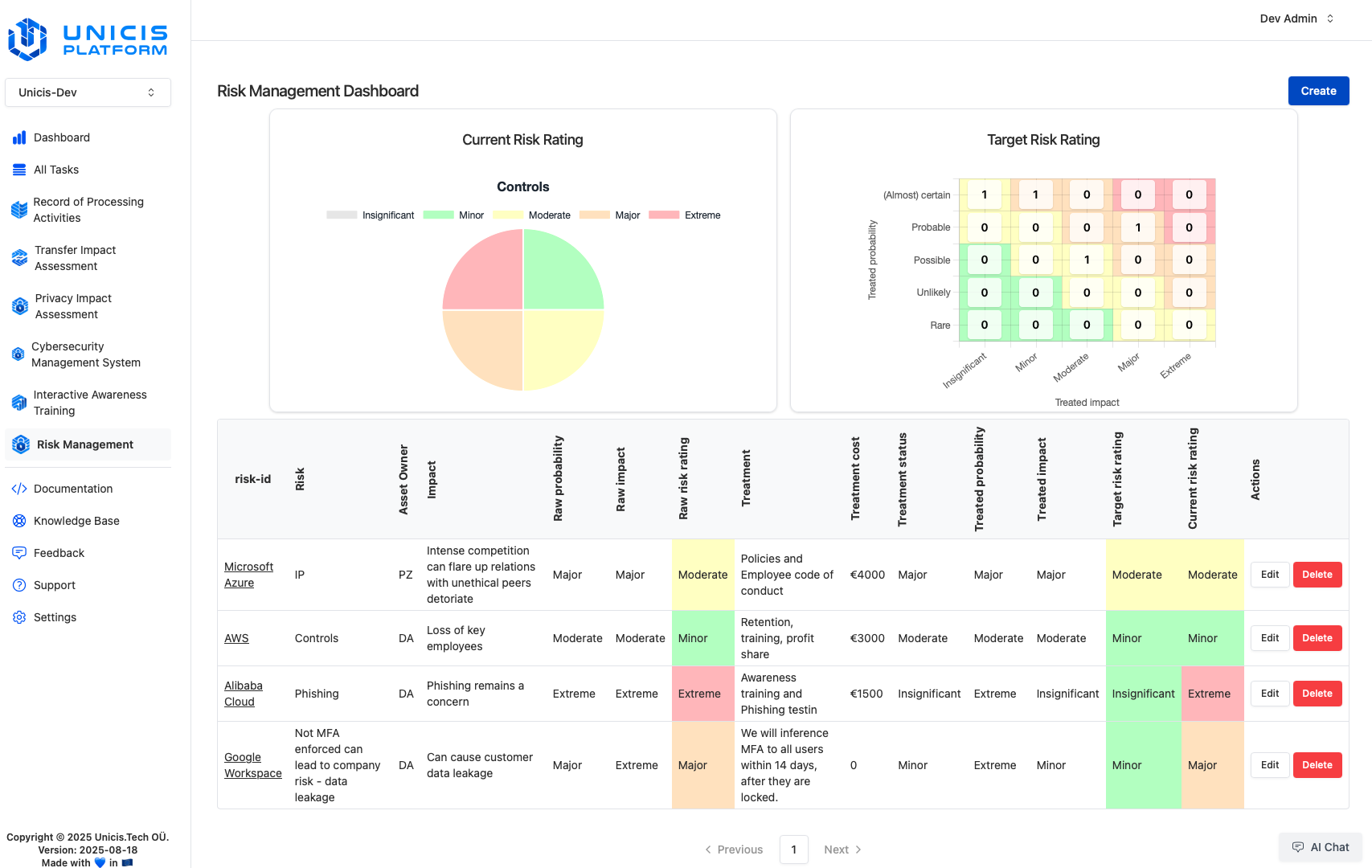
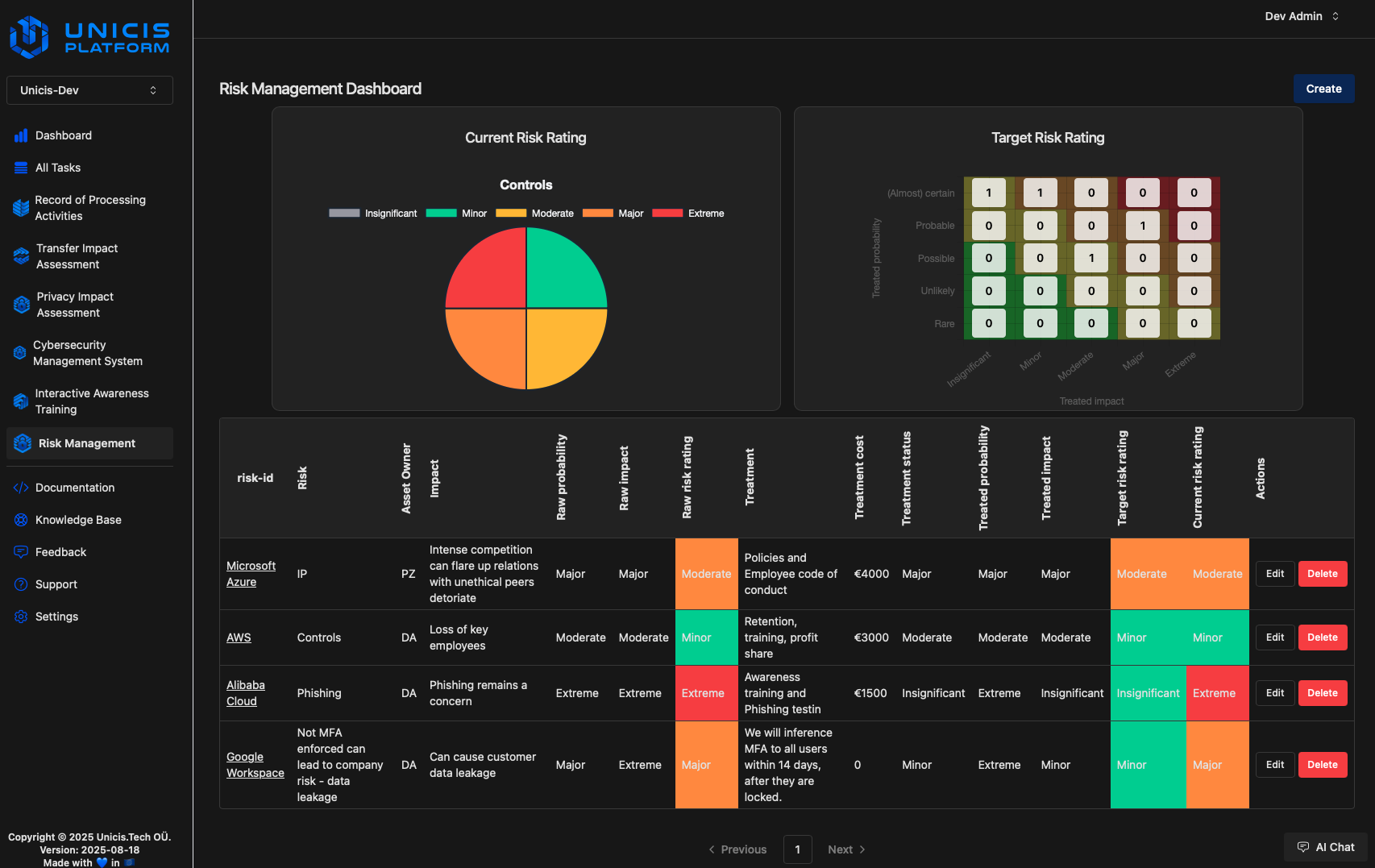
Dashboard Overview
The dashboard consists of two sections:
-
Risk Rating Charts
- Current Risk Rating Chart: Displays the current level of risk based on the implemented risk treatments.
- Target Risk Rating Matrix: Represents the expected risk levels after full implementation of controls.
-
Risk Register Table
- ID: Unique identifier for each risk, corresponding to a Task ID.
- Risk Description: Brief summary of the identified risk.
- Asset Owner: The responsible individual for managing the risk.
- Impact: Describe the potential business impact if the risk occurs, consistently using either worst-case or anticipated impact.
- Raw Probability: Likelihood of the risk occurring without any treatment (percentage value).
- Raw Impact: Estimated business impact without any treatment (percentage value).
- Raw Risk Rating: Product of the raw probability and raw impact.
- Risk Treatment: Strategy for mitigating the risk (avoid, transfer, accept, or control implementation).
- Treatment Cost: Estimated cost for mitigating the risk.
- Treatment Status: Implementation progress of the planned risk treatment (0%-100%).
- Treated Probability: Expected likelihood of the risk occurring after treatment, displayed in bold if different from raw probability.
- Treated Impact: Expected business impact after mitigation efforts, displayed in bold if different from raw impact.
- Target Risk Rating: The expected risk level after full implementation of controls.
- Current Risk Rating: The present risk rating based on the implementation progress of mitigation actions.
- Notes: Additional context or assumptions made during risk assessment, and can me added to Tasks description or Comments.
Risk ratings use conditional formatting with color scales (green, amber, red) for values ranging from 0% to 100%.
Risk Assessment Methodology
The risk register provides a systematic and systematic approach to identifying, assessing, and managing information security risks. Organizations can use it to document risks, evaluate their likelihood and impact, prioritize them based on severity, and decide on appropriate mitigation strategies. This methodology is aligned with ISO/IEC 27001 and ISO/IEC 27005:2022, which ensure a consistent and transparent risk management process. This is a starting point, but it can be changed to fit an organization's specific needs. You can change the risk criteria, calculation methods, and other things like compliance and how things work together. By changing how they approach cybersecurity, businesses can make sure they have enough resources and are ready for new threats.
Risk Calculation
The assessment follows the formula:
Risk = Probability × Impact
Probability and impact values are expressed as percentages. While this approach is not mathematically rigorous, it is effective in ranking and prioritizing risks for management decision-making.
Alternatively, organizations may use:
Risk = Threat × Vulnerability × Impact
This approach may be beneficial when historical data is available to assign quantitative values, particularly for frequently occurring incidents (e.g., data entry errors, malware, spam).
Risk Treatment Options
- Avoid: Eliminate the risk by discontinuing the activity.
- Transfer: Share the risk with another party (e.g., insurance or outsourcing).
- Accept: Recognize the risk and monitor it without active mitigation.
- Control Implementation: Apply security measures to reduce probability and/or impact.
Conduct sensitivity analysis using different formulas, data points, and assumptions to gain deeper insights. However, avoid "analysis paralysis"—risk management should prioritize action over excessive assessment.
Activity Logs
Audit logs track all risk modifications and can be accessed from the associated ticket under Audit logs > Risk Audit logs.
Logged changes include:
- Created
- Deleted
- Updated